JMeter Distributed Testing Step-by-step
JMeter Distributed Testing Step-by-step

This short tutorial explains how to use multiple systems to perform stress testing. Before we start, there are a couple of things to check.
- The firewalls on the systems are turned off.
- All the clients are on the same subnet.
- The server is in the same subnet, if 192.x.x.x or 10.x.x.x ip addresses are used. If the server doesn’t use 192 or 10 ip address, there shouldn’t be any problems.
- Make sure JMeter can access the server.
- Make sure you use the same version of JMeter on all the systems. Mixing versions may not work correctly.
Once you’ve made sure that the systems are ready, it’s time to setup remote testing. The tutorial assumes you already have JMeter installed on all of the systems. The way JMeter works is 1 master controller initiates the test on multiple slave systems.
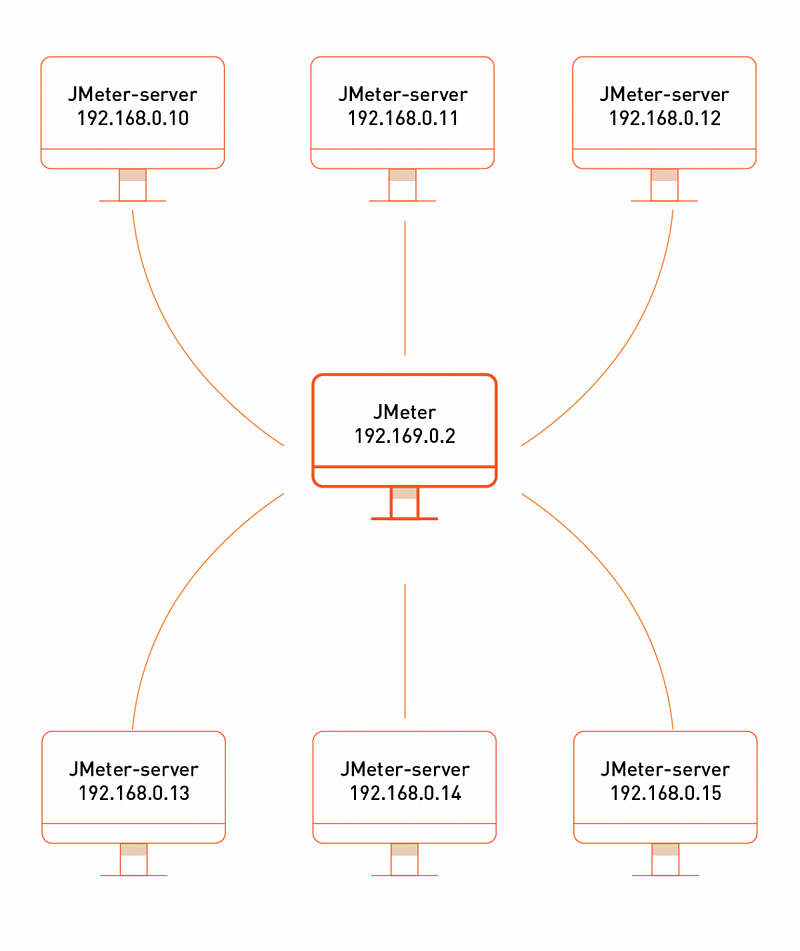
Terminology
Before we dive into the step-by-step instructions, it’s a good idea to define the terms and make sure the definition is clear.
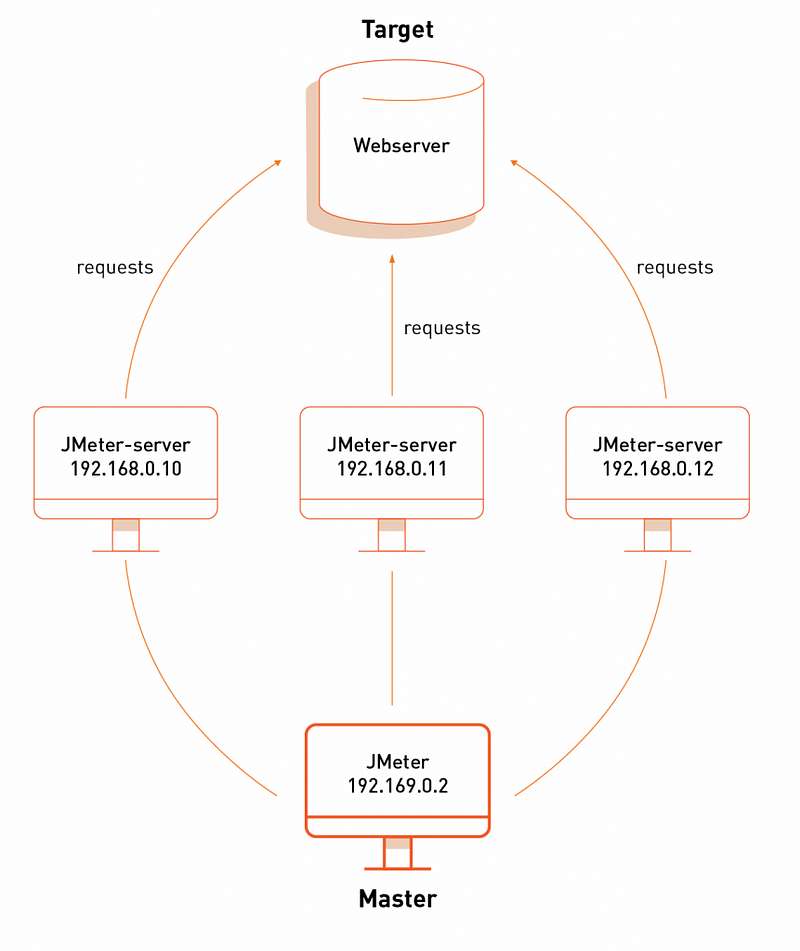
Master — the system running Jmeter GUI, which controls the test
Slave — the system running jmeter-server, which takes commands from the GUI and send requests to the target system(s)
Target — the webserver we plan to stress test 1/4
Step-by-Step
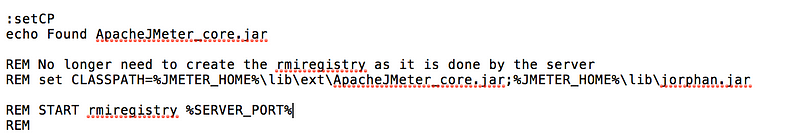
- On the slave systems, go to jmeter/bin directory and execute jmeter-server.bat (jmeter-server on unix). On windows, you should see a dos window appear with “jre\[version]\bin\rmiregistry.exe”. If this doesn’t happen, it means either the environment settings are not right, or there are multiple JRE installed on the system. Note: [version] would be the jre version installed on the system.
- Open jmeter-server.bat in a text editor
- go to line 47 and find “:setCP”
- edit “START rmiregistry” to the full path. Example: “START C:\\jre\bin\rmiregistry”
2. On master system acting as the console, open windows explorer and go to jmeter/bin directory
3. open jmeter.properties in a text editor
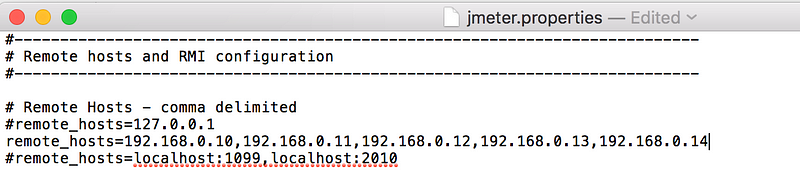
4. edit the line “remote_hosts=127.0.0.1”
5. add the IP address. For example, if I have jmeter server running on 192.168.0.10, 11, 12, 13, and 14, the entry would like like this: remote_hosts=192.168.0.10,192.168.0.11,192.168.0.12,192.168.0.13,192.168.0.14
6. Start jmeter.
7. Open the test plan you want to use
Starting the Test
At this point, you are ready to start load testing. If you want to double check the slave systems are working, open jmeter.log in notepad. You should see the following in the log.
Jmeter.engine.RemoteJMeterEngineImpl: Starting backing engine
If you do not see this message, it means jmeter-server did not start correctly. For tips on debugging the issue, go to the tips section. There are two ways to initiate the test: a single system and all systems.
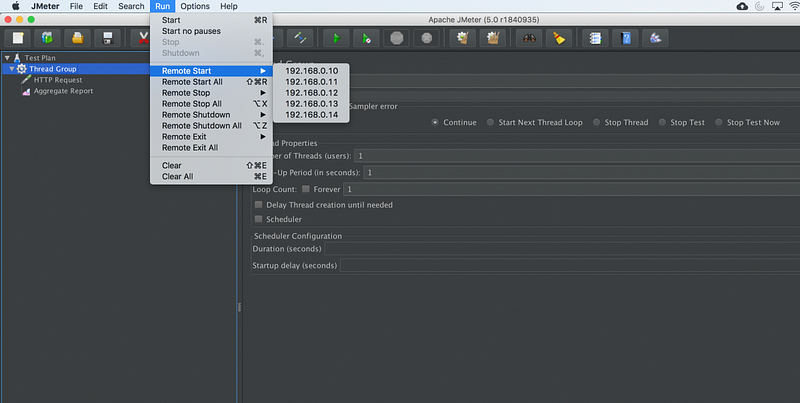
Start a single clients
- click Run at the top
- select Remote start
- select the IP address
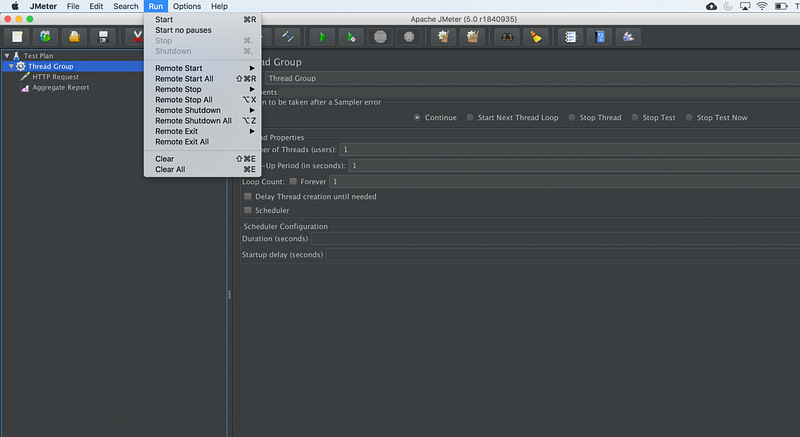
Start all clients
- click Run at the top
- select Remote start all or use CRTL-Z
Limitations
- There are some basic limitations for distributed testing. Here’s the list of the known items in no specific order.
- RMI cannot communicate across subnets without a proxy; therefore neither can jmeter without a proxy.
- Since JMeter sends all the test results to the controlling console, it is easy to saturate the network IO. It is a good idea to use the simple data writer to save the results and view the file later with one of the graph listeners.
- Unless the server is a large multi processor system, in most cases 1–2 clients is sufficient to overwhelm the server.
- A single JMeter client running on a 2–3Ghz CPU (recent cpu) can handle 300–600 threads depending on the type of test. (The exception is the webservices). XML processing is CPU intensive and will rapidly consume all the CPU cycles. As a general rule, the performance of XML centric applications will perform 4–10 slower than applications using binary protocols.
Additional resources
http://wiki.apache.org/jmeter/JMeterFAQ#How_to_do_remote_testing_the_.27proper_way.27.3F
http://jmeter.apache.org/usermanual/remote-test.html
Tips
In some cases, the firewall may still be blocking RMI traffic. Symantec Anti Virus and Firewall
In some cases, Symantec firewall needs to be stopped from windows services.
- open control panel
- open administrative tools
- double click services
- Go to down to symantec anti virus, right click and select stop
Windows firewall
- open network connections
- select the network connection
- right click and select properties
- select advanced tab
- uncheck internet connection firewall
Linux
On Suse linux, ipchains is turned on by default. For instructions, please refer to the “remote testing” in the user manual.
On RedHat (or derivatives), iptables (netfilter) is turned on by default. Execute “service iptables stop” to stop the Linux netfilter firewall.